
SEO Audit — What Marketers Need To Know
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a marketing technique almost as old as the internet. SEO has been declared dead multiple times. It’s not. You need to work at it. The best place to start is an SEO Audit.
What’s an SEO Audit?
An SEO Audit is a process that evaluates the performance of your website in search engines. There are 3 main parts of an SEO audit: Onsite, offsite, and technical.
The following are some of the criteria checked:
- Single site domain.
- Title tag and description.
- Proper indexing.
- Backlinks.
- Page speed and performance.
- Duplicate content.
- Much more…
It’s a lot. Let’s go through this together.
- What are your goals?
- What’s the effort to perform an SEO audit?
- How often should an SEO audit be done?
- Should I do SEO myself?
- What benefits do I get from an SEO audit?
- The criteria evaluated in a common SEO Audit
- What’s different with a full SEO Audit?
- Download the common SEO Audit checklist
What are your goals?
The first place to start is to determine what you want from SEO. Increasing traffic to your website is the most common goal. But not all traffic is created equal. Not all traffic does the same thing.
Do you want your website to generate more leads?
Are you looking to generate awareness?
Are you selling directly?
Do you want to increase your conversions?
SEO can help with all of your goals. You need to commit to SEO for it to work. Putting what you want in writing helps to make your intentions real.
What’s the effort to perform an SEO audit?
There are many different types of SEO audits. Neil Patel shows how to do a technical SEO audit in 1 hour. Ahrefs can show you how to perform a 16-step SEO audit. There are sites that will do a scan and return a result. They all work depending on what you want to accomplish.
SEO isn’t a one-off project. It is an ongoing effort. Different audits are good for different situations. A comprehensive SEO audit is where you need to start. Quicker audits are great to run monthly. They can catch things quickly. More in-depth audits work better each quarter.
To have the most success with SEO, you need someone focused on the effort. Your competitors aren’t going to stop trying to rank higher in Google. Being ranked in the top 5 of Google search results has a large positive impact on your business. It is competitive. The time you spend on SEO and audits should reflect its value.
How often should an SEO audit be done?
As we’ve touched on above, SEO is constant. There is no secret trick. There is no shortcut. It is constant work.
For audits, you should be doing small audits monthly. This audit can focus on things that may change more often. For example, page speed is something to monitor as you add features. Checking for broken links, titles, and descriptions are all things to keep track of.
In addition to a monthly audit, a more in-depth audit should be done quarterly. Search engines adjust how they index and ranking factors. Doing quarterly evaluations can help to keep current.
Finally, a full audit should be done yearly. This is the most in-depth audit. Use it to create a plan for the upcoming year. You won’t be able to tackle everything. Focus on the things that can positively impact your goals first.
Should I do SEO myself?
Do you have the time and resources to successfully perform SEO? If so, then you absolutely should do SEO for yourself. There are plenty of resources to get started from great sources. Here are some resources for performing an SEO audit:
- A 16-step audit process from Ahrefs.
- how to perform the world’s greatest SEO audit from Moz.
- How to perform an SEO audit in 18 steps from Semrush.
This post also provides a checklist of what we do as an initial audit that you can download or read below. These resources are not 100% comprehensive. As you perform your own SEO audit you will understand what you need to do specifically for your business. That’s why we always perform a full SEO audit before creating our playbook.
How to do your own SEO audit
Start with your goals. As we discussed above, understand what you want from your SEO. Your goals will help you focus your SEO audit on the things that are important to your business.
You are going to want to do a full audit. The audit should cover all 3 areas: Onsite SEO, offsite SEO, and technical SEO. Use the resources linked, use the checklist provided, and do some research. You should have a good starting point with the resources provided. While doing the audit, log what needs to be fixed. Put them into an order of importance. We like to use a simple grid: Low hanging fruit, long-term initiatives, not worth the effort, and big impacts.
I highly recommend using some tools to help yourself out. We use Ahrefs for our work. Moz or Semrush are both great options. Pick something you are comfortable with. They all have trials. You will be using these tools often.
Once complete, create a plan. Use the grid to begin your work. Some items like fixing website performance issues are going to require time from developers. You should be using some task planning tool. You may have one. If not, Saaslist has a good list of free kanban board tools you can use.
We’ve found the most intensive parts of an audit are the following:
- Content audit
- Site performance
- Checking for indexing issues
- Thin content analysis
Expect your audit to take some time. Give yourself 4 weeks or more to complete the audit. Don’t rush it. The better your audit, the better results you will get.
If you get stuck, reach out. We’ll be happy to point you in the right direction.
Getting help with your SEO audit
You may not want to go through the SEO audit process yourself. Time, people, and expertise are always factors. Not to worry, you can find great help.
You need to look for a few things when considering getting help from an agency or contractor.
- Expertise with SEO
- Willing to talk with you and discover your needs
- Can handle all 3 types of SEO from this post
- Can run a full SEO audit
- Honest about results
- Creates a plan and documents the audit
- Can implement the SEO suggestions including technical
- Can support your SEO efforts for the long-term
- Able to communicate without the jargon
It is difficult to rank in the top 5 of search results. It takes time and dedication. Even with that, there is no guarantee. Avoid anyone that guarantees results.
Pay particular attention to guarantees of reaching the number 1 result in search. Bad SEO is far worse than no SEO. If someone doesn’t follow what is recommended by Google, you may get delisted. This means that no results will show up for your business. The cost of that is catastrophic.
There are many good agencies and contractors out there. They won’t be the least expensive. They probably won’t be the fastest. Do your due diligence.
We offer a free initial SEO audit. That way you can evaluate our work with no risk. We can communicate and make sure there is a good fit.
Many other agencies or contractors will also offer free audits. The ability to try before you buy will help you understand the different capabilities of each. Avoid anyone that sends you random emails with a downloadable report.
What benefits do I get from an SEO audit?
An SEO audit is only valuable if search is part of your marketing strategy. That includes voice search. Don’t waste money when search is not a priority investment or budget consideration.
The audit produces a plan or what we call a playbook. The playbook outlines the different steps to be taken with specific actions for your business. The playbook provides detail so that you can perform the actions yourself.
The audit should detail what was reviewed, the methodology, and the tools used. An audit is educational. It presents a current state of your search performance and proposes a future state. In addition to the detailed analysis an audit should have an executive summary. Something that can be used for internally selling your need.
The criteria evaluated in a common SEO Audit
SEO audits vary in scope. To keep it simple we’ll use the terms common and full audit. A common audit is quicker to perform. It can be done without direct access to your website or consultation. It is what we use for our free audit.
The common SEO audit isn’t as detailed as a full audit. Some considerations take time to research. Some require access to your website code. Other considerations are collaborative. There are two parts to the common SEO.
General SEO Evaluation
General SEO is onsite and offsite SEO. Onsite are the things that you can change on your website like headings. Offsite are things you don’t control and are more difficult to impact.
The common SEO audit is going to focus on onsite items.
Single Version of Your Website
There are usually multiple ways to get to your website. One is with secure address. Another is with the older insecure address. For example — http://kalyber.com vs http://kalyber.com. Some websites may have the www subdomain. For example — https://www.kalyber.local or http://www.kalyber.local.
Every visitor should go to the same website address. The recommendation is the secure address without www. In our case that would be http://kalyber.com.
Why?
Google can see the different versions of the web address as duplicate content. First, that may impact your search ranking. Second, you may wind up with search results that have different web addresses. You can use a 301 redirect to fix this issue and have a single true web address.
Evaluate the Title Tag
The title tag is the bold text displayed in search engine results. It also appears on tabs on your browser. Consider yourself much more organized than me if you can see titles in your browser tabs!
The rules are simple: Well written, has valid keywords, and it doesn’t get truncated in search results.
Why?
Think of your title tag as an advertisement. It needs to be catchy and informative to get clicked. Top ranking pages on Google have high click through rates.
If you are using WordPress both RankMath and Yoast have a preview built-in for the title that checks keywords. You can also use a tool such as SERPsim to check your title online.
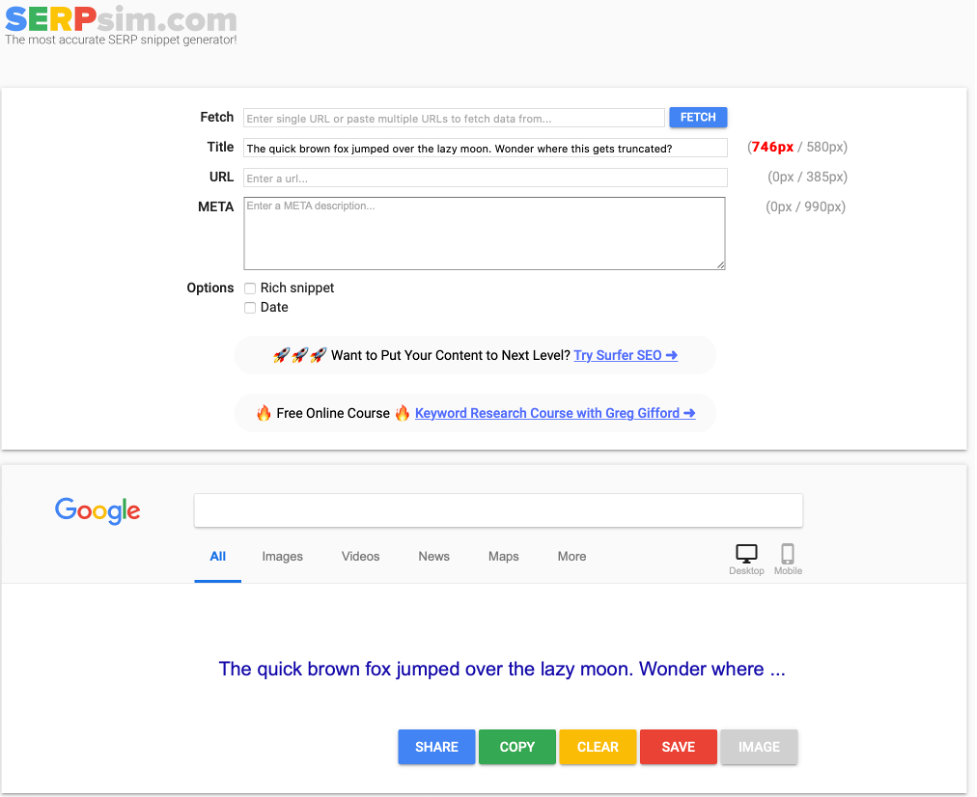
Evaluate the Meta Description Tag
The meta description tag isn’t a direct factor in search rankings. But, like the title tag you want people to click on your link. Click through rate is an important factor in SEO. The same rules apply for the meta description as the title tag.
The meta description should be longer than the title tag. RankMath, Yoast, and SERPsim all are good tools for checking the length of your meta description.
Get your headings right
Your content needs to be organized and readable. Your heading tags (h1, h2, h3, etc.) are an important part of organizing a page.
While it isn’t frowned upon to have multiple h1 tags, use only 1. Consider the h1 your main topic. If you have 2 of them, your content probably isn’t well focused.
Use keywords in your heading tags. But don’t force it. First, make sure a human can read it and understand your organization. The headings should be browsable. Allow someone scrolling to stop at a point that may interest them.
Use an SEO Analyzer
These tools crawl your website to look for on page SEO errors. We use Ahrefs for this purpose. Screaming Frog is a popular choice as well. Unlike a manual audit, these tools crawl your entire site. Perhaps a blog post doesn’t have a meta description. The tool will find these errors across your entire site for you.
Check for Duplicate Content
Google may penalize you for duplicate content. There are two kinds of duplicate content. Content that you have in two areas of your website and content that may have been copied by another site.
There are several tools that can help identify duplicate content. Ahrefs has a tool that will crawl your website for duplicate content. We also use CopyScape to scan the web for duplicate content.
If you are using common language in your cookie disclosure, terms and conditions, and other common content there is little to worry about. You’re looking for content that has been scraped in whole such as blog posts.
Validate What’s Being Indexed
The number of results in Google should match the number of pages you expect to be indexed for search. The fast way to check is to use Google Search Console. This will tell you exactly how many pages you have indexed.
If you don’t have access to Google Search console, you can run a site search on Google. This is done by using the site: operator like so — site:kalyber.com. You will get a result with all of the pages Google has indexed for the specific site.
Next, you want to cross reference the results. Again, we turn to Ahrefs. Ahrefs has a site audit we can use. Even better we can see errors that were found when the site audit was run. For example, redirects, 404 pages, etc. We are looking for any noindex tags. This will tell which pages are not being indexed.
You may find more content indexed in Google than what is being returned. This could be due to several issues. You may have duplicate content or Google may be indexing pages you don’t expect. A good example is many sites use deep structures for organization. For services companies it is common for a URL such as abc.com/services/service1.html. The services page may be blank but indexed. It should be fixed.
A big problem would be if you see no pages indexed by Google. This would likely mean an issue with how you defined your robots.txt, unreachable content, or other potential issues.
Do You Rank For Your Brand Name
If you are in the unfortunate position of having a common word as a company name, this will be a challenge. Google is good at figuring out the context. But if your company name is Apple you’re in trouble. Less popular common names can be overcome with some effort.
In other cases, your brand name should be the first result that shows up. New companies may take some time for this to happen. You need to create content that gets indexed.
If you’re an established company without a common name and are not showing up it could indicate a penalty. To find out you need to go to Google Search Console. You should find a message of No manual webspam actions found. The other issue could be an indexing issue as we discussed above.
Technical SEO Evaluation
Technical SEO deals with actions that will involve some kind of development knowledge. A common example is optimizing JavaScript or how it is loaded on the page. Others, while technical, can be addressed with tools. An example would be image compression.
Review Your Page Speed
How important is page speed? According to a June 2020 study by Google for mobile, a 0.1% increases lead generation rates by 5.5%. See the below image from Think with Google.

Why do I use mobile statistics? Google has been signaling for years that mobile is important. As of March 2021 mobile-first index will be the norm. It is a bit of a misnomer as well. It is mobile only indexing. So mobile performance matters.
Why else is page load times important? Another Google update for May 2021 is the page experience update. This includes page load times as a factor in rankings.
You may read that page speed and load times aren’t the most important factors to focus on for SEO. We do know that bounce rate and conversion rate do matter. Research in 2018 by Pingdom on how load time affects bounce rates is summed up in their chart below.
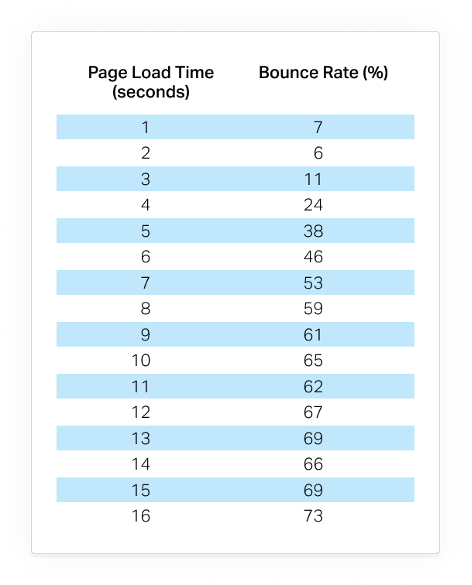
You need well-written relevant content. You also need to make sure it loads fast enough for people to actually see it. You need to convert. Everything plays a part in how Google ranks your content for search.
There are many ways to check the performance of your website. A simple way is using your browser’s developer tools. There are two tools in Chrome. We’ll take a look at the network tab. There you will see all of your resources loaded for the website and how long it takes.
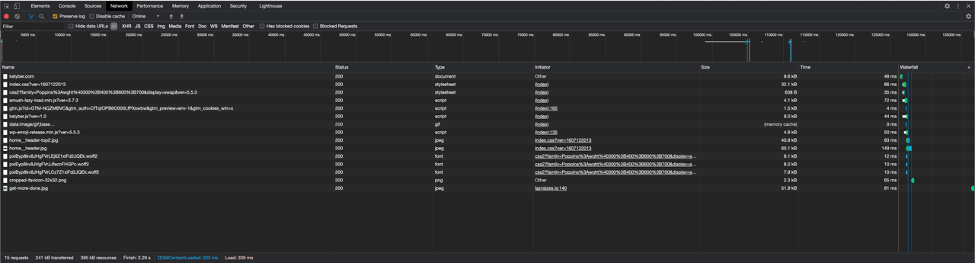
The above is a snapshot of our home page after clearing the cache. The DOM (HTML structure) too 233ms to load. Load of the page was 339ms. The total for full download was 2.29 seconds. Each line in the table is a resource and its size. Large images are a typical problem for slow loading sites.
Slow websites are easy to spot. They tend to flash or the content shifts as everything is loaded. That isn’t a great user experience. Always think about how you would react visiting your own website for the first time.
Google PageSpeed Insights
This tool from Google is helpful in checking your website against Google’s page experience. In May 2021 page experience will be a ranking factor for search results. The update uses core web vitals with interesting names to determine the page experience. In human terms, it is how long before someone sees your website, is able to interact with it, and does it shift a lot as it loads. You’re looking for fast, fast, and not at all.
PageSpeed Insights is where you can test your website for these metrics. The image below shows the results of our core web vitals before optimization.
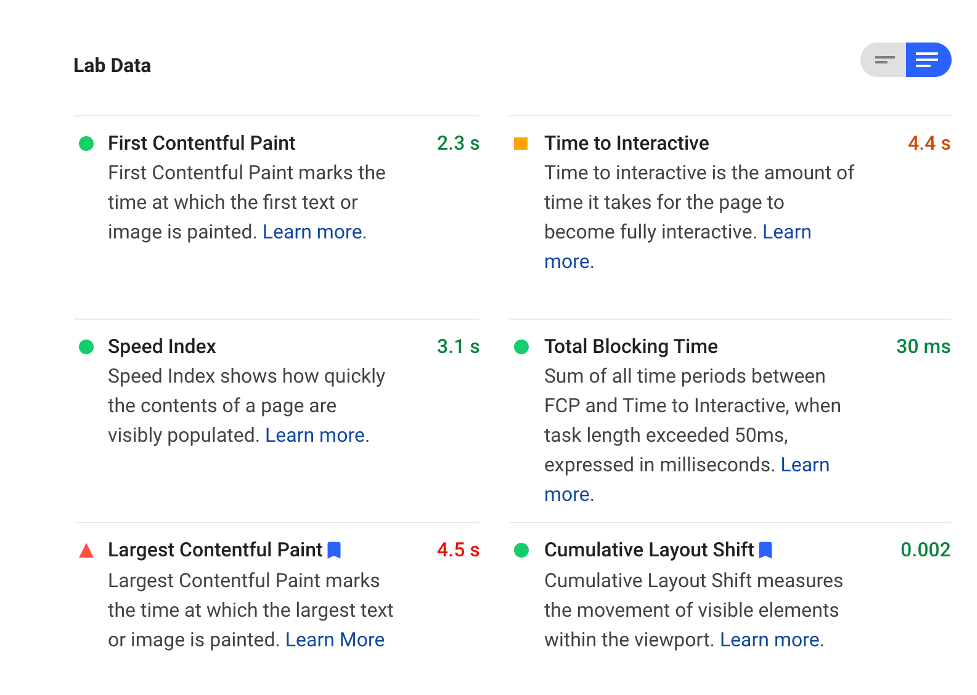
The tool provides suggestions on how to fix some errors. In our case, we know we have a large CSS and font loading that blocks rendering. That is the top suggestion for improving Time to Interactive. Don’t overoptimize and sacrifice UI or UX. A fast, terrible website will not help your SEO.
You can get more in-depth information about PageSpeed Insights and performance from our posts on the topic:
- PageSpeed Insights.
- PageSpeed Insights with WordPress.
Robots Settings
Robots tell crawlers such as Google and Bing how to view your website. There are two main ways to tell them how to crawl — on the page and in a robot.txt file.
To control a specific page, you use the meta robots tag. If you are using WordPress, both RankMath and Yoast allow you to set this from within WordPress. In other systems, you would need to rely on the developers to have implemented something for you.
The robots.txt files control indexing for your entire website. A common problem when no indexing is done is the robots.txt. Many companies have at least a staging website and a production website. No one wants the staging website to be indexed. The robots.txt file reflects that. It accidentally gets moved with updates to the live website. Google is no longer indexing your website.
Keywords Review
We’ll provide to you the keywords you rank best for and the estimated amount of traffic they drive. This uncovers content issues, keyword gaps, and overall search performance.
We’ve worked with customers where branded hosted content gets indexed and ranked. An example would be a company that sets up a portal for their customer’s employees to purchase company-branded swag. People forget the login page and go to Google. Now the business ranks for the keyword Lowe’s swag login. Not helpful to your efforts.
These kinds of keyword mismatches happen more often than you think. We use Ahrefs to run a report on the keywords you rank for. We sort based on ranking position and traffic.
Review Your Sitemap
An XML sitemap provides a structure overview of your content to search engines. The benefit of having a sitemap is that it provides a secondary source for search engines to crawl.
A simple mistake like forgetting to link to a new page in your menu would cause a search engine to not index that page. It would also miss any pages that only link from that page. A sitemap would tell the search engine the pages exist and to crawl them.
Another scenario could be landing pages. You don’t link to them on your website. You do want them crawled and indexed. If the page is in the sitemap, you’re all set.
WordPress automatically creates a sitemap now. Plugins do it as well. Other systems may require development to automatically update a sitemap.
Make Sure You Have Structured Data
Structured data provides additional information about a page. This is particularly useful for reviews, products, events, and other content that may warrant more information.
You want to make sure you are using structured data and that it is correct. Google has a rich results test to help.
For example, search for any product. For the Apple HomePod Mini we get a result from BestBuy that has ratings, price, etc. Below is the result of the rich results test.
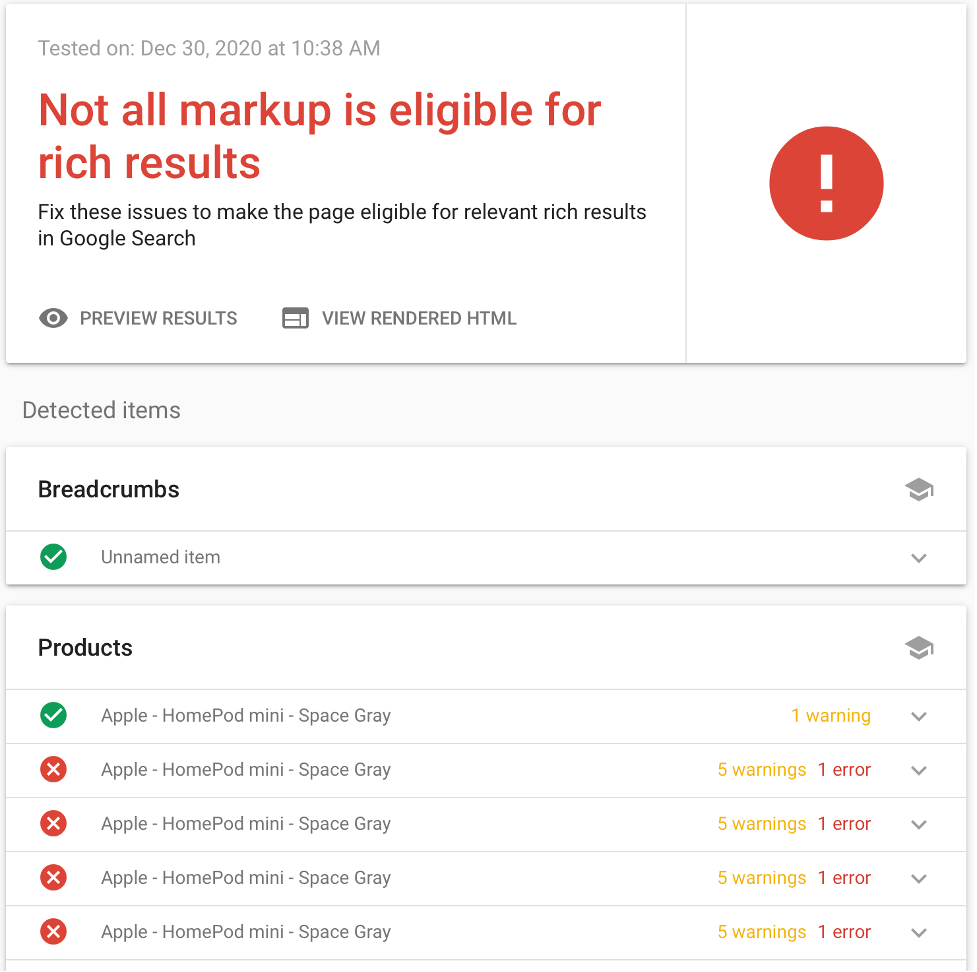
Find Broken Links
Broken links are bad for multiple reasons. A visitor clicking on a link that doesn’t work is a terrible experience. Google tries to index broken links and lowers link equity. Broken links should be fixed immediately.
SEO professionals use your broken links to their advantage. They provide great backlink opportunities and easy opportunities for ranking for different keywords.
There are multiple tools you can use to find and fix broken links. We use Ahrefs for this purpose.
Find and Fix Orphan Pages
An orphan page is a page that isn’t linked to from your website. You want to avoid orphan pages so that you can build link equity across your website. Your site may have pages that are intentionally not linked and can be ignored.
How do you discover orphan pages? We turn to Ahrefs again and the site audit. The report will let us know which pages do not have internal links.
Basic Mobile Rendering Check
Google has prioritized mobile for search. This is a simple check of your most important pages. You want to make sure that the pages render in mobile. You want to make sure that all of the important content is included in the mobile version of the page.
We’ve seen cases where content is hidden on a mobile view to save space. Removing content that isn’t important like a signup button is fine. Removing content that has keywords and is relevant to the visitor is a red flag.
Full SEO Audit
A common SEO audit seems like a lot. What more can we possibly check? A full SEO audit takes everything from our common audit and goes into more depth. There are certain things we can only review with access to your Google Analytics and Search Console.
A full SEO audit includes more advanced SEO techniques. For example, your search competitors may not be your business competitors. Below are some of the additional considerations for a full SEO audit.
Content Review
A content review goes through your content and analyzes it for some key factors. This will check for thin content — pages that have little to no words. Pages should have at least 200 words. Long content is usually preferred.
A content review will go through existing content and recommend content that should be purged. Old content can hurt your overall rankings in search. Updating the content or removing it is often beneficial.
Organic Search Review and Analysis
An evaluation of your current organic search results provides a baseline. The goal is to determine how well you rank for your keywords. The analysis looks at performance over time and if your results are increasing or decreasing.
Backlink Analysis
Backlinks are an important signal in search rankings. Looking at your backlinks and your search competitors’ backlinks help determine what needs to be done. It identifies opportunities for backlinks and provides a signal for the content people are looking for.
Content Gaps
Content gaps are areas where your competitors are ranking for keywords that you are not. Identifying content gaps helps to create a content schedule and topics to focus on. Looking for content gaps can help identify a change in the market early.
For example, a keyword may not have a large search volume today. In our content gap analysis, we see competitors ranking for a new keyword with low volume. The change is worth monitoring. In some cases, it is worth creating content for.
An example would be returning to work during the summer of months of COVID-19. There was a large uptick in content focused on this keyword by one of the competitors of our customer. Shortly, it was driving a lot of traffic and a competitive keyword.
Competitor Analysis
Our audit focuses on two kinds of competitors — business and keyword. Your business competitors are well known. Your business competitors may not be good at SEO. We compare your performance to that of your business competitors. It helps to uncover industry keywords, even if your business competitors aren’t focused on SEO.
Your business competitors may not be your keyword competitors. You could be competing against an industry expert for keywords.
Our case is a perfect example of keyword competitors. Many of our business competitors either don’t do SEO for themselves or are just not good at it. From a search perspective, they aren’t competitors. SAAS products and industry experts are great at SEO.
Ahrefs is not a business competitor. We use their product. Ahrefs is a keyword competitor for us. We discuss similar topics about the community we work with. I’ve linked to their posts on this very topic in this post. Your keyword competitors are more important for search than your business competitors.
UX Review
We’ll take a deeper look at the user experience of your website. This is a factor for Google in search. Large popups can be bad for UX. Menus that are difficult to use. Some UX will hurt your conversion rates.
Canonical and Multilingual
A canonical link is the page that should be considered the main page. For search engines it says don’t index this page, go to this URL and index the page specified. This is done to avoid duplicate content.
We all try to avoid duplicate content, but it happens. We can try to update the information architecture to solve the problem, but making sure there is proper usage of canonical links solves the problem.
If you have a site that serves multiple pages using the hreflang meta tag is important. We check to make sure that the tag is present and works as expected.
Broken Link Building
Using broken links is a way to quickly garner rankings for a keyword. It is also why we suggest fixing your broken links immediately. We identify opportunities to use your competitor’s broken links to create content and gain backlinks.
Information Architecture Review
Our review of your Information Architecture (IA) checks the depth of your website. Long URLs and nested pages can create a poor user experience. Your site structure needs to make sense. It needs to be easy for search engines to crawl.
Image Analysis
Images are important for SEO for many reasons. The filename should be descriptive. The alt tag should have your keyword. Good image descriptions not only help SEO but are good for screen readers and voice search.
Mobile Rendering
Mobile will be the default and only way Google indexes your website in the near future. It is important that all content is rendered. There cannot be issues with how the page is rendered on mobile devices. You need to think about your content in terms of mobile and how it will impact search.
Download the common SEO Audit checklist
There is a lot to an SEO audit. To help we’ve created an SEO audit checklist you can download. The checklist has the most common SEO areas to review. You can use it as a guide to be sure you don’t miss anything.
Still have questions? Reach out and we’ll do our best to answer your answers fully. You can contact us here or connect on social media: twitter: @jdela13 or @kalyberhq linkedin: James de la Bastide or Kalyber Instagram: @kalyberhq facebook: @kalyberhq
Continue Reading
seo Audit
Uncover problems impacting your search results.
SEO Audit Checklist
Download your SEO audit checklist and learn how to do your own audit.
Free Audit
